XGap Technology

Xgap technology is a multi-gap core approach for transformers and inductors developed in-house to reduce AC losses in the windings that allows for the creation of cost-effective solutions for maximum power densities.
What is Xgap Technology?
- The multi-gap technology has been developed by PRAX to reduce winding AC losses.
- It allows to use big gaps distributed around the toroid to minimize fringing effect.
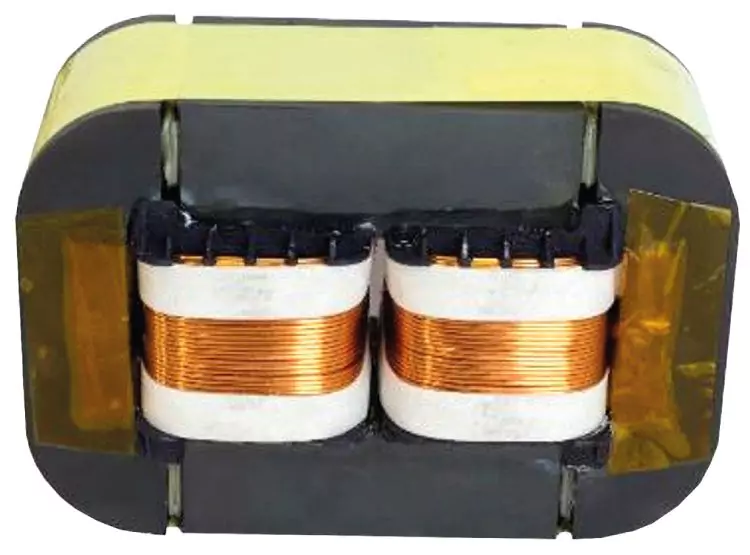
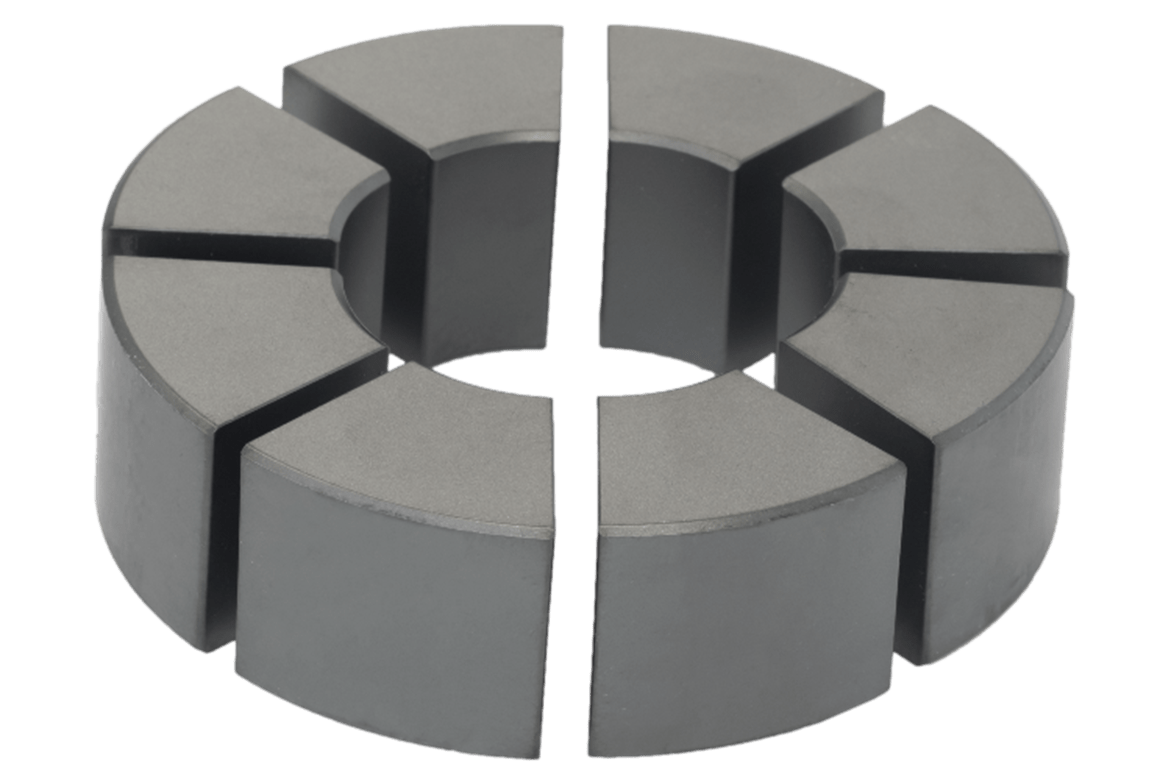
- It consists on splitting a big gap into smaller gaps. These smaller gaps are distributed around the toroidal core.
- Losses are reduced exponentially when we use up to 12-15 smaller gaps because of Rac reduction.
Advantages of Xgap Technology
- Gap distributed component, minimizing fringing losses.
- Increases winding area by using toroid formats. Not needed to keep windings far away from the gap.
- High current and high frequencies handling by means of using low losses ferrite material
- Best dissipation of windings in any type of cooling systems
- Tighter tolerances for the inductance value (from ±25% to ±10%)
- Reduction of core volume around 30%, allowing an overall size reduction of around 15-20% Cost-effective solution (i.e. compared with PQ or PM format)
 Prax introduces technology as an optimal solution for high demanding applications
Prax introduces technology as an optimal solution for high demanding applications
The use of xgap technology allows for the creation of cost-effective solutions with maximum power density thanks to the reduction of core volume around 30%, while overall size reductions up to 20%.
xgap technology also minimizes losses and offers optimal heat dissipation of windings in all type of cooling systems. All of these advantages match the requirements of magnetic components in demanding applications, such as EV chargers or resonant converters.
What is xgap technology based upon? 
A gap is a portion of air inside a magnetic core path. It is used for two main purposes:
1. Energy storage in inductors or chokes
The energy stored in an inductor depends on current and inductance factor.
A gap or distributed airgap is commonly needed in cores to store such energy.
2. Inductance value and tolerance reduction
Introducing a gap decreases magnetic core permeability, which reduces its inductance factor.
Non-gapped cores inductance tolerance is around ±25%, while gapped cores can be reduced to ±10%
Main effects generating losses due to high frequency in windings
 1. Skin effect
1. Skin effect
An isolated round conductor carrying AC current generates a concentric alternating magnetic field which induces Eddy Currents.
These currents oppose to normal current flow in the center of the conductor, increasing the effective current closer to the conductor surface.
The overall effect is that total current flows in a smaller perimetral area. This effect intensifies as frequency increases. Current flow concentrates in an equivalent perimetral cylinder at the surface of the conductor. This cylinder thickness δ is known as skin depth.

2. Proximity effect
Proximity effect appears when the distribution of current in one layer of a winding influences the distribution in another layer, always in the same winding.
Such proximity effect, therefore, increases winding resistance (Rac)
3. Fringing effect
Fringing effect happens when a magnetic flux near a core airgap bends out.
The distance over which these flux fringes out is basically proportional to the length ofthe airgap.
One single gap can be splited into several smaller gaps, preserving total volume and length. By doing so, effective permeability and energy storage capabilities are still the same, but the flux fringing is significantly reduced.
Advantages of the xgap technology
- Winding area increases by means of using toroid formats
- High current and high frequency capabilities by low losses
- ferrite material
- Distributed gap component, minimizing fringing losses
- Tighter inductance tolerance (from ± 8% to ± 15%)
- Best heat dissipation of windings in any type of cooling systems
- Finite Elements Analysis (FEA) simulations available for extra accurate loss calculation
- Reduction of core volume around 30%, allowing an overall size reduction up to 20%
- Cost-effective solution compared with PQ or PM core formats