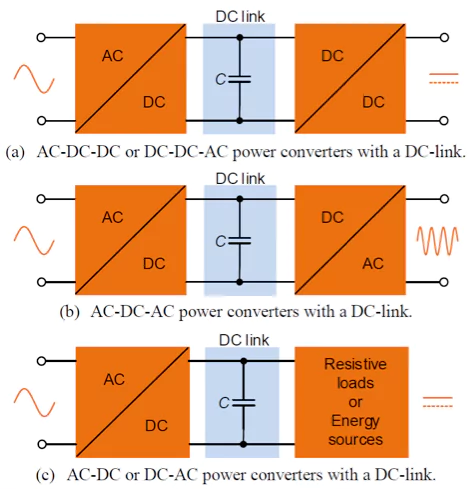
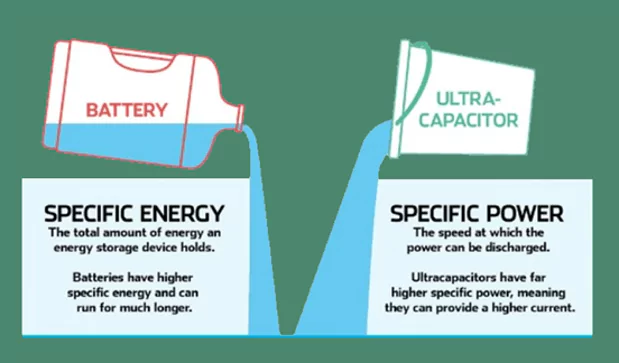
Snubber Capacitors in the Field

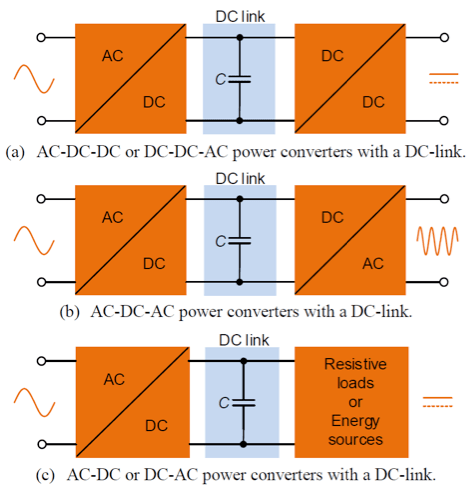
Given that snubber capacitors address the negative impacts of switching, it’s no surprise that they’re most commonly found in switching power supplies. These systems face major challenges from switching, including:
- Switching transients
- Parasitic elements
- High-frequency noise
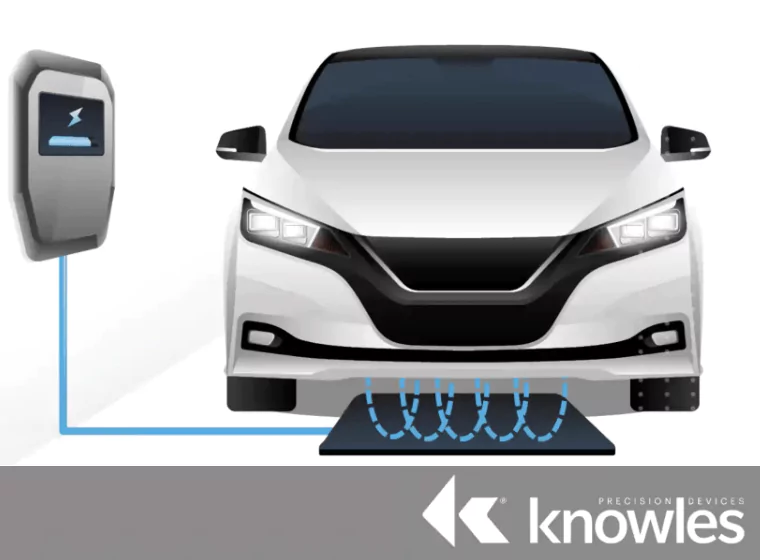
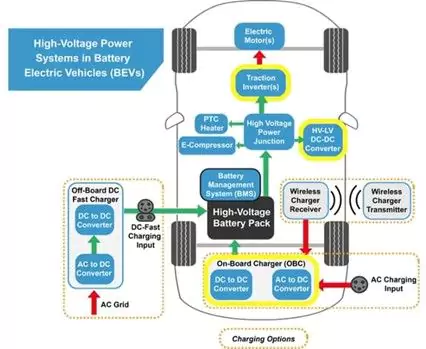
AC to DC conversions in electric vehicles (EVs) is a great example. Insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBT) are used for fast and efficient switching in power electronics, including EV inverters. These inverters are responsible for converting DC battery power to three-phase AC power, which drives the traction motor during acceleration, and converts AC power back to DC power when the vehicle is braking.
A power module that’s responsible for a three-phase load will need at least six IGBTs and six snubber capacitors to protect the semiconductors appropriately. These snubbers protect power switching in EVs by absorbing noise.
Today, we’re starting to see more power supply circuits with wide-bandgap semiconductors, rather than the traditional IGBTs, mentioned above. While the fundamental circuit design process remains the same, substituting a component as vital as a semiconductor impacts component selection across the board—including snubber capacitors.
With the shift towards wide-bandgap semiconductors, engineers need to step back and take a fresh look at factors like voltage rating, capacitance value, equivalent series resistance (ESR) and equivalent series inductance (ESL) in the design process.